| Royal Australian Navy | |
| http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Naval_Ensign_of_Australia.svg/250px-Naval_Ensign_of_Australia.svg.png The Australian White Ensign | |
| Founded | 10 July 1911 |
| Country | Australia |
| Branch | Navy |
| Part of | Australian Defence Force |
| Naval Headquarters | Russell Offices, Canberra |
| Size |
30 ships, about 20,000 personnel |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the Naval Staff | Vice Admiral Raymond Griggs, AM, CSC |
| Vice Chief of the Naval Staff | Rear Admiral Trevor Jones, AM, CSC |
| Commander Australian Fleet | Rear Admiral Steve Gilmore, AM ,CSC |
| Insignia | |
| Navy Crest | http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/a/a3/RAN_badge.png/100px-RAN_badge.png |
| Ship classes | |
| Aircraft carriers | Australia class |
| Cruisers | Hobart class |
| Destroyers | Battle class, Ballarat class |
| Frigates | ANZAC class, Adelaide class |
| Submarines | Collins class |
| Patrol craft | Armidale class, Pacific class |
| Amphibious ships | Wellington class, Kanimbla class, Balikpapan class |
| Auxiliaries | Success class, HMAS Sirius, HMAS Endeavour |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Fighter/Ground Attack | AV-8X |
| AEW | Sea King AEW Mk. 57 |
| ASW Helicopter | S-70B-2, S-70B-9 |
| VERTREP | Sea King Mk 50, S-70A-44 |
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the naval branch of the Australian Defence Force. Established in 1911, the RAN was formed out of the Commonwealth Naval Forces to become the small navy of Australia after federation, consisting of the former colonial navies of the new Australian states. The Royal Navy of the United Kingdom continued to provide blue-water defence in the Pacific until World War II, when expansion of the RAN saw the acquisition of aircraft carriers, and other large surface vessels.
After World War II, the RAN was focussed on forward defence in South East Asia, therefore the RAN was structure to provide a carrier battle group to a NATO, or SEATO command. This was centred around the carrier HMAS Melbourne. After withdrawal from Vietnam, Australia changed its focus to a Two-Ocean Navy which would operate indpendently in home defence.
This was to be focussed around 2 carrier battle groups (one for the Pacific Ocean, the other for the Indian Ocean) with 4 large destroyers (the term 'cruiser' was avoided for political reasons, however the ships sought had a displacement of over 9000 tons), patrol vessels in the North, and submarines for survellance, interdiction, and special forces support. This led to an expansion and modernisation of the RAN.
In the event, the 'large destroyers' were not proceeded with until the mid-1990s, by which time they were ordered as Guided Missile Cruisers
The Daring class destroyers to be replaced and the Perth class guided missile destroyers were to be supplemented by a new guided missile destroyers. The new destroyers, the Ballarat class, were based on the British Type 42 destroyer, but with American weapons, and a different layout.
Two frigate roles were defined, escort and patrol. The RAN determined that to fulfill both roles, that at least 12 frigates were required. The patrol role was less important, and River class frigates were transferred to this role as Adelaide class frigates became available to replace them as escorts. The admission of New Zealand into the Commonwealth of Australia increased by frigate force by two ships, HMNZS Waikato and HMNZS Canterbury, which were similar to the RAN's existing River class destroyer escorts.
By 1990, the Royal Australian Navy had a substantial combat force force including:
- 2 Australia class Aircraft Carriers (R)
- 4 Ballarat class Guided Missile Destroyers (DDG)
- 3 Perth class Guided Missile Destroyers (DDG)
- 6 Adelaide class Guided Missile Frigates (FFG)
- 6 River class Destroyer Escorts (DE)
- 2 Leander class Frigates (F)
- 6 Oberon class Submarines (SSG)
- 15 Fremantle class patrol boats (PB)
Today the RAN is one of the largest naval forces in the Pacific region and has a significant presence in the Indian Ocean, and has undertaken operations in support of military campaigns and peacekeeping missions worldwide.
Today's fleet consists of around 60 vessels including cruisers, destroyers, frigates, submarines, patrol boats and auxiliary ships. The RAN today is one of the most modern in the Pacific and is tasked with the ability to defend Australian waters and undertake operations in distant locations.
The RAN's major ships are derivatives of Western designs. They frequently include Australian improvements, for example, the Adelaide class Frigates are based on the American Oliver Hazard Perry frigates, but include such improvements as an 8-cell Mk 41 VLS for Evolved Sea Sparrow Missiles. Unlike American ships, they retained their Mk 13 launchers, the capabilities of which are extended by the integration of SM-2MR, and Harpoon Block II.
Australia's Hobart class cruisers are Australian made conbatants based on the American Ticonderoga class. They are considered among the most powerful surface combatants in the world.
The ANZAC class Frigates were originally intended as light patrol frigates by the Labor government of the late 1980's, but have been progressively upgraded. Upgrades include adding an extra 8 Mk 41 VLS cells (bringing the total to 16), adding 8 Harpoon launchers, and a new mine avoidance system. An active phased array radar is slated for installation from 2009.
The RAN has two primary bases for its fleet;
- Fleet Base East, which is located at HMAS Kuttabul near Sydney, NSW.
- Fleet Base West, located at HMAS Stirling near Perth, WA.
In addition, there are three other ports which are home to the majority of the RAN's minor war vessels (patrol craft, mine warfare craft);
- HMAS Coonawarra, at Darwin, NT.
- HMAS Cairns, at Cairns, QLD.
- HMNZS Philomel, at Devonport, NZ.
Vice Admiral Sir Russ Shalders, AK is the current Chief of the Naval Staff and was appointed to this position in 2005.
All Royal Australian Navy ships and shore stations use the prefix Her Majesty's Australian Ship. Some shore establishments in New Zealand retained the designation Her Majesty's New Zealand Ship, but all warships were redesignated in 1988.
Combat organisation[]
The surface fleet is organised into two Carrier Battle Groups (CBG East, and CBG West), each based on an Australia class aircraft carrier, and four Surface Action Groups (SAG Alpha, SAG Bravo, SAG Charlie, SAG Delta), each based on a Hobart class cruiser. Each battle group has a Battle class destroyer, and one or two frigates assigned
Current Fleet[]
(see Ship profiles page)
Major Combatants[]
- 2 Australia class Aircraft Carriers (R) [1]
- HMAS Australia
- HMAS Vengeance
- 4 Hobart class Guided Missile Cruisers (CG) [2]
- HMAS Hobart
- HMAS Brisbane
- HMAS Perth
- HMAS Achilles
 HMAS Australia |
 HMAS Vengeance with USS Wasp, USS Forrestal, and HMS Invincible |
 HMAS Brisbane |
 HMAS Achilles |
Destroyers[]
- 3 Battle class Guided Missile Destroyers (DDG) [3]
- HMAS Gallipoli
- HMAS Long Tan
- HMAS Coral Sea
- 4 Ballarat class Guided Missile Destroyers (DDG) [4]
- HMAS Ballarat
- HMAS Toowoomba
- HMAS Lismore
- HMAS Goulbourn
 HMAS Gallipoli, a Battle class destroyer underway |
 HMAS Coral Sea in profile with an S-70B-2 helicopter |
 HMAS Long Tan launches an SM-2 missile |
 Artist's impression of the Ballarat class Destroyer |
Frigates[]
- 10 ANZAC class Frigates (FFH) [5]
- HMAS ANZAC
- HMAS Te Kaha
- HMAS Arunta
- HMAS Te Mana
- HMAS Warramunga
- HMAS Stuart
- HMAS Parramatta
- HMAS Blackpool
- HMAS Otago
- HMAS Waikato
- 6 Adelaide class Guided Missile Frigates (FFG) [6]
- HMAS Adelaide
- HMAS Canberra
- HMAS Sydney
- HMAS Darwin
- HMAS Melbourne
- HMAS Newcastle
Minor Combatants[]
- 16 Armidale class Patrol Boats (PB) [7]
- HMAS Armidale
- HMAS Larrakia
- HMAS Bathurst
- HMAS Albany
- HMAS Pirie
- HMAS Maitland
- HMAS Ararat
- HMAS Broome
- HMAS Bundaberg
- HMAS Wollongong
- HMAS Childers
- HMAS Launceston
- HMAS Hawea
- HMAS Pukaki
- HMAS Rotoiti
- HMAS Taupo
- 4 Pacific class Light Patrol Boats (PBL) [8]
- HMAS Tarangau
- HMAS Dreger
- HMAS Seeadler
- HMAS Basilisk
- 6 Huon class minehunters (MHC) [9]
- HMAS Huon
- HMAS Hawkesbury
- HMAS Norman
- HMAS Gascoyne
- HMAS Diamantina
- HMAS Yarra
Submarines[]
- 8 Collins class Submarines (SSG) [10]
- HMAS Collins
- HMAS Farncomb
- HMAS Waller
- HMAS Dechaineux
- HMAS Sheean
- HMAS Rankin
- HMAS Goldsworthy
- HMAS Osborne
 Collins class submarine HMAS Rankin snorting |
 HMAS Collins, lead ship |
 HMAS Rankin with USS Key West |
 The former HMAS Torrens - sunk by a Mark 48 torpedo from HMAS Farncomb |
Amphibious Warfare Ships[]
- 2 Wellington class Landing Helicopter Dock (LHD) [11]
- HMAS Wellington
- HMAS Auckland
- 3 Manoora class Landing Platform Dock (LPD) [12]
- HMAS Manoora
- HMAS Kanimbla
- HMAS Tobruk
- 8 Balikpapan class Landing Craft, Heavy (LCH) [13]
- HMAS Balikpapan
- HMAS Brunei
- HMAS Labuan
- HMAS Tarakan
- HMAS Wewak
- HMAS Salamaua
- HMAS Buna
- HMAS Betano
Fleet Auxiliaries[]
- 2 Success class Replenishment Oilers (AOR) [14]
- HMAS Success
- HMAS Endurance
- 1 Fleet Oiler (AO) [15]
- HMAS Sirius
- 1 Fleet Oiler (AO) [16]
- HMAS Endeavour
- 1 Sail Training Ship (IX)
- STS Young Endeavour [17]
- 3 Leeuwin class ocean survey vessels (AGS) [18]
- HMAS Leeuwin
- HMAS Melville
- HMAS Monowai
- 6 Paluma class coastal survey vessels (SML) [19]
- HMAS Paluma
- HMAS Mermaid
- HMAS Shepparton
- HMAS Benalla
- HMAS Resolution
- HMAS Tui
- 1 Diving Tender (A) [20]
- HMAS Manawanui
Fleet Air Arm[]

Fleet Air Arm S-70B-2 Seahawk
see main article: Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (more formally known as the Australian Navy Aviation Group) is the operational part of the Royal Australian Navy responsible for the operation of aircraft aboard ship. The FAA is currently an mixed force, operating helicopters, and strike fighters in both the following roles.
- Fleet Air Defence
- Anti-Surface Warfare
- Land Attack
- Anti-Submarine Warfare
- Reconnaissance
- Vertical Replenshment
- Coastal maritime patrol
- Amphibious Operations (transport of troops and supplies, aerial fire support, and air defence)
Clearance Diving Teams[]

Clearance Divers on a boarding exercise

Clearance Divers emerge from the water
The Clearance Diving Teams (CDT) of the Royal Australian Navy also act as commando frogmen: they consist of naval personnel who are qualified in diving, demolitions, underwater repairs, and reconnaissance. Clearance Divers can deploy from surface ships, aircraft, and submarines. They fulfil a Maritime Counter-Terrorist role as part of the waterborne troop of the Tactical Assault Group East (TAG EAST).
The Clearance Diving Teams are usually under the control of Australian Special Operations Command.
The CDT's have the following roles
- Mine Counter Measures (MCM) and Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD), including:-
- Location and disposal of sea mines in shallow waters
- Rendering safe and recovering enemy mines
- The search for and disposal of ordnance below the high water mark
- Clearance of surface ordnance in port or on naval facilities
- Search for, rendering safe or disposal of all ordnance in RAN ships and facilities, including the removal of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)
- Maritime Tactical Operations including:-
- Clandestine hydrographic survey of an amphibious beach
- Clandestine clearance or demolition of sea/land mines and/or obstacles
- Clandestine placing of charges, demolitions for the purpose of diversion or demonstration
- Underwater Battle Damage Repair
- Support of TAG EAST (4RAR (Cdo)) in maritime terrorist incidents
List of Clearance Diving Teams[]
- Clearance Diving Team One (AUSCDT ONE); assigned to the east of Australia and based at HMAS Waterhen in New South Wales
- Clearance Diving Team Four (AUSCDT FOUR); assigned to the west of Australia and based at HMAS Stirling in Western Australia
- Clearance Diving Team Three (AUSCDT THREE) (formed from personnel of both teams on combat deployments)
There are also ten Reserve Teams (RDT) that provide reinforcements to the regular teams.
- Reserve Diving Team Six - Victoria
- Reserve Diving Team Seven - Western Australia
- Reserve Diving Team Eight - Southern Queensland
- Reserve Diving Team Nine - South Australia
- Reserve Diving Team Ten - Tasmania
- Reserve Diving Team Eleven - Northern Territory
- Reserve Diving Team Twelve - Northern Queensland
- Reserve Diving Team Fourteen - New Zealand
- Reserve Diving Team Fifteen - Solomon Islands
Commissioned Shore Establishments[]
- HMAS Kuttabul - Fleet Base East
- HMAS Stirling - Fleet Base West/NAS West
- HMAS Albatross - NAS Nowra
- HMAS Waterhen - Mine Warfare and Clearance Diving Group
- HMAS Cairns
- HMAS Coonawarra
- HMNZS Philomel
- HMNZS Wakefield
- HMAS Harman - Naval Communications Area Master Station Australia
- HMAS Creswell - Royal Australian Naval College
- HMAS Cerberus - Royal Australian Navy Recruit School
- HMAS Penguin
- HMAS Watson - Radar Training School
[]
Guns[]
- 5 in (127 mm) Mk 45 Mod 2/4 gun
- OTO Melara 76 mm/62 caliber naval gun
- 30 mm DS30B rapid fire cannon
- Rafael Typhoon 25mm naval stabilised deck gun
- Mk 38 Mod 0 25mm Bushmaster cannon
- Mk 15 Phalanx 20mm CIWS
Missiles[]
- Standard Missile
- RIM-66K/M Standard SM-2MR
- RIM-156 Standard SM-2ER Block IV
- RIM-161 Standard SM-3
- RIM-174 Standard SM-6 ERAM
- RIM-7M Sea Sparrow
- RIM-116 RAM
- RIM-162 Evolved Sea Sparrow Missile
- RGM-84D/G/K Harpoon
- UGM-84D/G/K Sub-Harpoon
- BGM-109C/D Tomahawk
- RGM/UGM-103E Tactical Tomahawk
Torpedoes[]
- Mark 46 Torpedo
- MU90 Advanced Lightweight Torpedo
- Mark-48 ADCAP
Mines[]
- Mark 60 CAPTOR (Encapsulated Torpedo)
- Mark 67 SLMM (Submarine Launched Mobile Mine)
- MN103 - MANTA
- Stonefish mine
Australian White Ensign[]
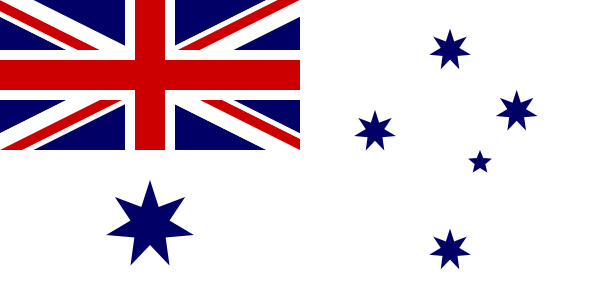
This is the Australian White Ensign, it is flown from all RAN commissioned ships, and all RAN commissioned shore establishments. It is also worn on overalls, flying suits, DPCU, and DPDU.
Uniforms[]
The Royal Australian Navy has several different uniforms. The Service Dress uniforms are generally identical to those worn by the Royal Navy, with the exception of the title "AUSTRALIA" appearing on jacket shoulders, and rank slides. Junior sailors however have a different summer uniform, consisting of straight line white trousers, and a button-up white shirt.
Most sailors wear a grey coverall with safety boots as a working dress. Blue cotton drill shirts (called Action Working Dress) and trousers can also be worn (generally ashore, grey tends to be worn on ship).
Clearance Divers are involved in ground combat, and therefore wear DPCU, or DPDU as their working dress. Other naval personnel are issued DPCU and DPDU as required.
Grey coveralls and AWD are being replaced with a fire retardant variation on DPCU called Disruptive Pattern Naval Uniform (DPNU). DPNU in the AUSCAM pattern, with various shades of grey and green replacing the greens and browns of DPCU.

Disruptive Pattern Naval Uniform (DPNU)
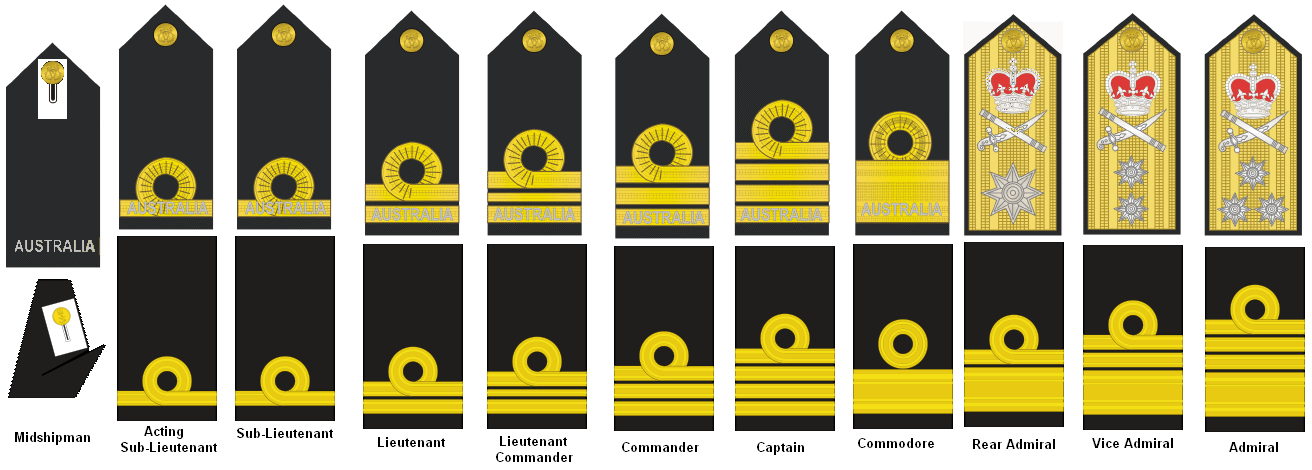
Rank Insignia[]
Service Dress[]
Officer Ranks[]
Petty Officers, and Seamen[]
N.B. There is an RAN rank of Admiral of the Fleet, however only the Duke of Edinburgh has ever held this rank, and it is not considered an operational RAN rank.
DPCU[]
Officer Ranks[]
Petty Officers, and Seamen[]
DPDU[]
Officer Ranks[]
Petty Officers, and Seamen[]
The Future[]
The Royal Australian Navy currently has requirements to replace the Australia-class aircraft carriers, and their aircraft. The RAN also requires replacements for the Kanimbla class amphibious transport ships.
Historical Gallery[]